In IoT, staying competitive means keeping devices secure, functional, and up to date—without costly manual interventions. Over-the-Air (OTA) updates solve this by enabling remote firmware upgrades, security patches, and feature rollouts at scale.
For businesses, OTA isn’t just a technical feature—it’s a strategic advantage. It reduces downtime, cuts maintenance costs, and mitigates security risks. In a world where outdated firmware can mean vulnerabilities or compliance failures, OTA updates are no longer optional—they’re essential.
What is OTA for IoT?
Over-the-air, or OTA, updates for the Internet of Things are like a dynamic duo that complement one another. An Internet of Things device with an OTA capability is refining its operation with the goal of minimizing the degree of human intervention required for setting up the device.
It lets businesses update devices remotely, whether it’s a single patch or a full software upgrade. Device maintenance and control are becoming easier because to this technology. Over-the-air updates let devices in the Internet of Things to remain updated with the newest security standards and software. OTA (Over-the-Air) updates let you push new software or firmware directly to your connected devices—no cables, no downtime, no on-site hassle.
Why OTA Updates Important for IoT Devices?
As previously said, OTA updates are enhancing the functionality of IoT devices by enabling users to update the firmware at any time and from any location. In the context of the Internet of Things, OTA updates are also crucial for maintaining and improving the performance, security, and functionality of a huge network of connected devices.
IoT devices are getting increasingly complicated, with software and hardware interacting in ways that necessitate frequent updates. In actuality, the software layer now accounts for an increasing portion of the product's worth. After devices have been distributed, manufacturers use OTA updates to make continuous improvements, from feature implementations to performance optimization.
Unlike controlled environments, consumer IoT devices operate in unpredictable ecosystems, interfacing with third-party hardware, smartphones, and dynamic Since not all compatibility issues can be detected by pre-launch testing, proactive software management cannot be subject to compromise. Teams can react swiftly, address issues in the field, and adjust to changes in the larger ecosystem with the help of OTA updates.
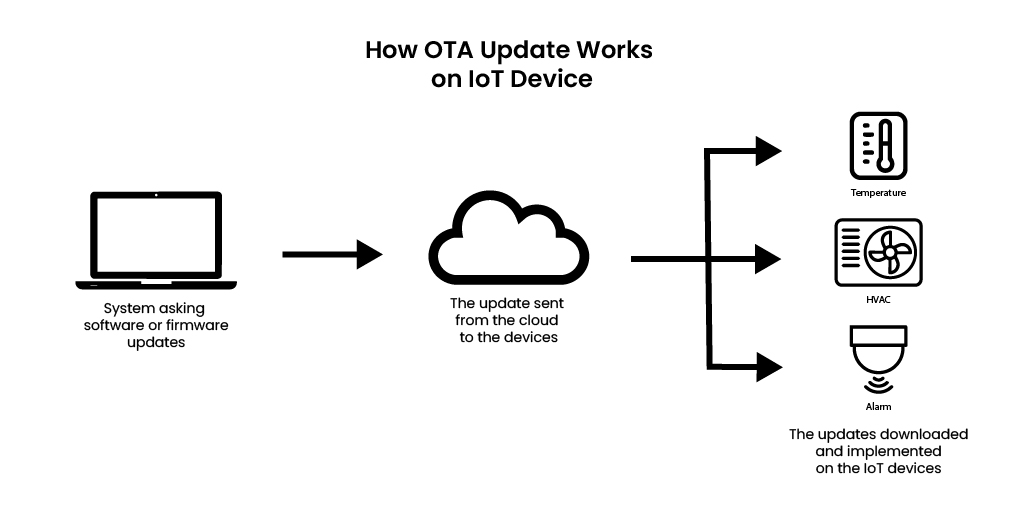
How OTA Update Works on IoT Device
Devices linked to the internet receive new firmware or software through OTA updates. They can be manually activated by engineers, staged for a phased deployment, or delivered automatically. To maintain security and stop unauthorized changes or corrupted firmware from interfering with operations, devices authenticate and check updates prior to installation. This procedure guarantees that gadgets stay safe and operational over the duration of their lives.
Both approaches make sense depending on the circumstances and the products involved, but moving from OTAs to manual updates or the other way around is rarely a sensible course of action. In the end, the initial choice must grow as you get more clients and sell more devices.
Common OTA update scenarios
Edge to Cloud
In this scenario, IoT devices at the edge (such as sensors or embedded systems) connect directly to the cloud to receive firmware or software updates. It is ideal when edge devices have internet connectivity and can communicate securely with the cloud platform.
Gateway to Cloud
Here, the gateway device itself receives OTA updates directly from the cloud. This is common in setups where the gateway plays a central role in managing multiple local devices and requires periodic updates to its own firmware or system software.
Edge to Gateway to Cloud
This is a hybrid model where edge devices communicate with a local gateway, which in turn connects to the cloud. The gateway manages updates on behalf of the edge devices, acting as an intermediary to distribute OTA updates efficiently, especially in environments with limited bandwidth or security constraints.
Asset OTA
Asset OTA refers to updating specific tracked assets—such as beacons, tags, or portable IoT devices—over the air. These updates help maintain performance, fix bugs, or apply security patches without the need to retrieve or manually handle each asset.
Benefit of OTA Updates for IoT
By implementing an OTA update, you could gain these following benefits:
Flexibility
With OTA, you can push updates from anywhere, no travel, no delays. Great for assets that are spread out over multiple locations or field-deployed.
Improved User Convenience
Maintenance is made hassle-free with remote updates, which eliminate away with the need for manual installation or in-person trips to service centers. By scheduling updates in less busy times, device performance can be maximized without interfering daily operation. Users may also have flexibility and convenience in scheduling updates, with the ability to delay or cancel them as necessary.
Cost Effectiveness
OTA updates save time and lower operating expenses by reducing the frequency to send the on-site technicians. Also, the downtime would be minimalized, since OTA updates can be done quickly, the process is only delayed for a short time.
Maintain Safety
Throughout their existence, they enable developers and operators to maintain devices safe, up-to-date and dependable by implementing new features, fixing vulnerabilities, and enhancing performance without interfering with business operations.
What are the main challenges in using OTA updates for IoT?
Like many other things, OTA updates present unique difficulties that organizations must overcome and that may use up resources, time, and money:
Provide Updates with Context Awareness
Devices may function differently depending on their settings, use cases, or situations. It's critical to make sure the correct update is compatible with the right device.
Plan for Connectivity Limitations
IoT devices frequently operate in remote, unstable, or low-bandwidth network environments. OTA solutions need to take into consideration sporadic connectivity and guarantee that updates can safely resume or retry.
Prepare for Recovery from Failures
Incomplete or unsuccessful upgrades may cause a device to stop working. In order to preserve uptime and save field service expenses, rollback mechanisms or fail-safes must be put in place.
Mitigate Security Risks
If OTA updates are not properly encrypted, they may turn into an attack target. Verified firmware, device authentication, and end-to-end encryption are essential for preserving trust and security.
Scale with IoT Deployments
It gets more difficult to manage updates across thousands or even millions of endpoints as the number of connected devices increases. Effective load balancing, grouping, and scheduling are important.
Learn from Real-World Feedback
OTA approaches need to change in response to field data and user behavior. Future rollout plans can be improved, and disruptions can be minimized by keeping an eye on update success rates, device health, and user feedback.
How We Support OTA at IoT Stadium
In Iot Stadium, we allow user to do an OTA update for their devices. We provide a feature called device models, where user may set some preset for particular types of device, which also they can edit or add some new firmware on that model.
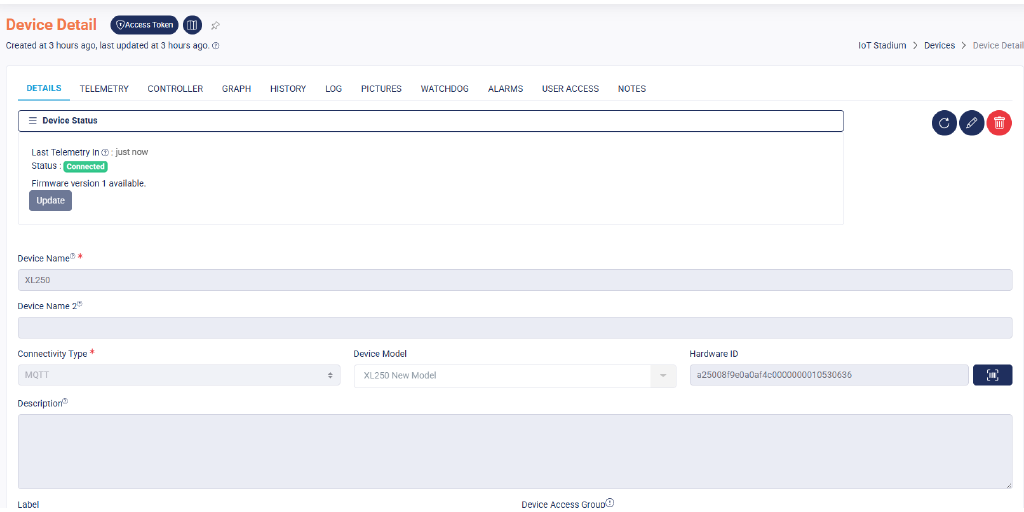
Like this example above, all the device under that model can be updated via OTA, which minimize the physical intervention and maintain the work efficiency. All the setting can be seen this article: Add Device Models.
Conclusion
Whether you’re managing smart sensors, industrial gateways, or remote healthcare monitors, OTA helps you move faster, stay safer, and stay in control. They complement each other, allowing users to update firmware or software remotely. These updates are crucial for maintaining and improving the performance, security, and functionality of a large network of connected devices. OTA updates can be manually activated, staged for deployment, or delivered automatically. They are essential for maintaining security and preventing unauthorized changes or corrupted firmware from interfering with operations. Challenges include providing updates with context awareness, planning for connectivity limitations, preparing for recovery from failures, mitigating security risks, managing updates across thousands or millions of endpoints, and learning from real-world feedback.
Visit our blog for more information about technology. Alternatively, visit our knowledge base page for tutorials on using the features in IoT Stadium.